JSON Files are one of the most used data formats for communication between two web applications. In this article, we will discuss what JSON objects are and how can we work with JSON files in Python.
- What is JSON Object?
- The Syntax For Defining JSON Objects
- Working with JSON Files in Python
- Python Object to JSON File
- Python Object to JSON String
- Python Object to JSON String Using JSONEncoder Class
- Load JSON Files to Python Object
- Convert JSON String to Python Object
- JSON String to Python Dictionary Using JSONDecoder Class
- Why Use JSON Files With Python for Data Transmission?
- Conclusion
What is JSON Object?
JSON is an acronym for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a standard text-based format for representing data in a structured manner using key-value pairs. It is most commonly used for transmitting data between web applications. The JSON files have .json extension.
Following is an example of a JSON object.
{"Name": "Aditya", "Age":23, "Height":181}What is a Nested JSON Object?
A nested JSON object is a JSON object containing another JSON object as the associated value for one or more keys. We can also use a nested JSON object for transmitting data. For example, consider the following JSON object.
{
"coffee": {
"region": [
{"id":1, "name": "John Doe"},
{"id":2, "name": "Don Josh"}
],
"country": {"id":2, "company": "ACME"}
},
"brewing": {
"region": [
{"id":1, "name": "John Doe"},
{"id":2, "name": "Don Josh"}
],
"country": {"id":2, "company": "ACME"}
}
}
The above JSON object is a nested JSON object. You can observe the following.
- In the outer object, we have two keys namely
“coffee”and“brewing”. - The
“coffee”and“brewing”keys contain other JSON objects as their values. Hence, the given JSON object is a nested JSON object. - Inside
“coffee”and“brewing”, we have two keys namely“region”and“country”. The“country”contains another JSON object as its key while the“region”contains a list of JSON objects.
So, a nested JSON object can contain another JSON object or a list of JSON objects.
The Syntax For Defining JSON Objects
As you can observe in the above two examples, a JSON object has the following syntax.
- The data is present in key-value pairs in a similar manner to a python dictionary.
- The keys and values in a JSON string are separated by a colon
(:). - Each key-value pair in a JSON object is separated by a comma
(,). - The entire data in a JSON object is enclosed by curly brackets
({ }). - The string values and keys are enclosed in double quotes
(“ ”). - The arrays are enclosed in square brackets
([ ]). - The values in an array are separated by a comma. The values in the array can be a JSON object, an array, or a literal of any permitted data type.
- The keys in the JSON object are of string data type. On the other hand, the associated values can be one of the permitted data types. The permitted data types are string, number, object, array, boolean or null.
Working with JSON Files in Python
Python provides us with the JSON module to work with JSON strings and files in Python. Let us now discuss how to convert a python object to a JSON object and vice versa.
Python Object to JSON File
We can convert a python object to a JSON file using the dump() method.
The dump() Method
The dump() method has the following syntax.
json.dump(python_obj, fp, *, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None, default=None, sort_keys=False, **kw)Here,
- The
python_objparameter takes a python object that needs to be converted to a JSON file. The object can be a number, string, dictionary, list, or custom python object. - The
fpparameter takes a file pointer as its input argument. After opening a file with a.jsonextension in write mode, you can pass it to thefpparameter. After execution, the contents of thepython_objare saved to the file pointed byfpin JSON format. - A key in a python object can be of any data type. However, all the data types cannot be converted to JSON format. When we try to create a JSON file from a python object or a dictionary with keys having data types other than
str,int,float,bool, andNone, thedump()method raises a TypeError exception. Theskipkeysparameter helps us handle data in such situations. When we setskipkeystoTrue, thedump()method skips the keys having incompatible data types instead of running into a TypeError exception. - The
ensure_asciiparameter is used to make sure that all the characters in the output JSON file are ASCII characters. Whenensure_asciiis set toTrue, all the non-ASCII characters inpython_objare skipped. If it is set toFalse, the non-ASCII characters are saved to the JSON file as is. - The
check_circularparameter is used to make sure that thedump()method performs circular reference checks for container types. Ifcheck_circularis set toFalse, the circular reference check is skipped. In this case, a circular reference will cause the program to run into RecursionError exception. - The
allow_nanparameter is used to convertNaNand infinity values to JSON format. Whenallow_nanis set toTrue, thedump()method convertsNaN,+inf, and-infto JavaScriptNaN,Infinity,-Infinityrespectively. Whenallow_nanis set toFalse, thedump()method raises a ValueError exception when it findsNaN,+inf, or-infinpython_obj. - The
clsparameter is used when we want to convert custom python objects to JSON. For converting a custom object to JSON, we need to define a customJSONEncodersubclass and pass it to theclsparameter. - The
indentparameter is used to specify the indentation in the JSON object. When theindentparameter is set toNoneor a negative integer, the JSON object is in the most compact representation. When theindentparameter is set to a positive integer value, it indents that many spaces per level in the JSON object created from thedump()method. When theindentis set to a string, the string is used as the indentation character. When theindentis set to 0 or an empty string, a new line is introduced for each level of indentation. - By default, the key-value pairs of a JSON object are separated by a comma and the key is separated from the values using a colon character. To specify a new separator for the keys and items, you can pass a tuple containing two characters to the
separatorsparameter. The first character of the tuple becomes the separator for the key and value. The second element of the tuple becomes a separator for different items. When theindentparameter is set toNone, the default value for theseparatorsparameter is(', ', ': '). Otherwise, the default value for theseparatorsparameter is(',', ': '). To get the most compact JSON object, you should remove whitespaces from the separators and use(',', ':')as an input argument to theseparatorsparameter. - When the
dump()method gets a non-serializable object in thepython_objparameter, it raises a TypeError exception. You can use thedefaultparameter to handle this case. Thedefaultparameter takes a function as its input argument. The function should return a JSON-encodable version of the object or raise a TypeError. - The
sort_keysparameter is used in thedump()method if you want the keys of the JSON object in a sorted manner. If thesort_keysparameter is set toTrue, the keys of the output JSON object are sorted in a lexicographic manner.
After execution, the dump() method saves the JSON file to the given file pointer. You can observe this in the following example.
import json
myStr="Aditya Raj"
fp=open("fromstring.json","w")
json.dump(myStr, fp)
fp.close()Output:
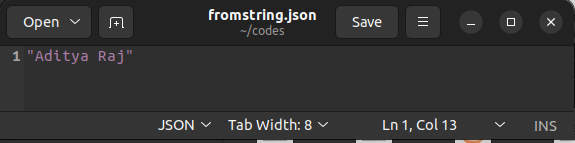
In the above example, we have converted the string "Aditya Raj" to a JSON file named fromstring.json. For this, we first opened the fromstring.json file in write mode using the open() function. The open() function takes the file name and the literal "w" as its input argument. After execution, it opens the file in write mode and returns a file pointer. We pass the file pointer and the input string to the dump() method. After execution, the dump() method saves the JSON object in the file.
Finally, we closed the file using the close() method. If you don’t close the file, any data written to the file will not be saved. Hence, it is an important step.
You can also convert objects like lists and dictionaries to JSON files using the dumps() method in Python as shown below.
import json
myDict={"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}
fp=open("fromdict.json","w")
json.dump(myDict, fp)
fp.close()Output:
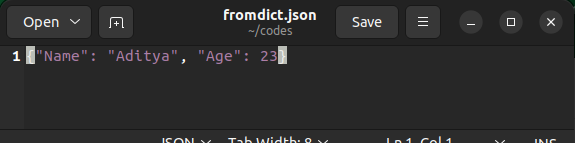
In this article, we have converted a python dictionary to a JSON file in python. Similarly, you can also convert a list to JSON file using the dump() method.
For converting custom python objects to JSON, you can read this article on custom JSON encoder in Python.
Python Object to JSON String
The dumps() Method
The dumps() method is used to convert a python object to a JSON formatted string. It has the following syntax.
json.dumps(python_obj, *, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None, default=None, sort_keys=False, **kw)All the parameters in the dumps() method have the same meaning as the respective parameters in the dump() method. The only difference is that the dump() method saves the JSON object to a file and the dumps() method returns a JSON formatted string after execution. You can observe this in the following example.
import json
myStr="Aditya Raj"
print("The input string is:")
print(myStr)
jsonStr=json.dumps(myStr)
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)Output:
The input string is:
Aditya Raj
The JSON string is:
"Aditya Raj"You can also convert objects like lists and dictionaries to JSON strings using the dumps() method in Python as shown below.
import json
myDict={"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}
print("The dictionary is:")
print(myDict)
jsonStr=json.dumps(myDict)
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)Output
The dictionary is:
{'Name': 'Aditya', 'Age': 23}
The JSON string is:
{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}Python Object to JSON String Using JSONEncoder Class
The JSONEncoder class is used to create default and custom JSON encoders for converting python objects to JSON format. The JSONEncoder() constructor, when executed, returns a JSONEncoder object.
We can invoke the encode() method on the JSONEncoder object to create a JSON string from a python object. The encode() method, when invoked on a JSONEncoder object, takes a python object as its input argument and returns the JSON representation of the python object. You can observe this in the following example.
import json
myStr="Aditya Raj"
print("The input string is:")
print(myStr)
jsonStr=json.JSONEncoder().encode(myStr)
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)Output:
The input string is:
Aditya Raj
The JSON string is:
"Aditya Raj"In this example, we first created a JSONEncoder object using the JSONEncoder() constructor. Then, we used the encode() method to convert a python string to a JSON string.
Instead of primitive data types, you can also convert container objects such as lists and dictionaries to JSON format as shown below.
import json
myDict={"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}
print("The dictionary is:")
print(myDict)
jsonStr=json.JSONEncoder().encode(myDict)
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)Output:
The dictionary is:
{'Name': 'Aditya', 'Age': 23}
The JSON string is:
{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}Suggested Reading: If you are into machine learning, you can read this article on mlops for beginners. You might also like this article on clustering mixed data types in Python.
Load JSON Files to Python Object
We can load JSON files to python objects using the load() method.
The load() Method
The syntax for the load() method is as follows.
json.load(fp, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)- The
fpparameter is the file pointer to the file object containing the JSON file. - The
clsparameter is used when we want to convert JSON to a custom python object. For converting JSON to a custom object, we need to define a custom JSONDecoder subclass and pass it to theclsparameter. - The
object_hookparameter is used to create custom JSON decoders. Theobject_hookparameter takes a function as its input argument. The function is called with the object literal decoded from the JSON. In the output, the return value of the function is used instead of the dict. - The
parse_floatparameter is used to convert any floating point number in the JSON to another data type. By default, thefloat()function is called with the strings containing floating point numbers in the JSON. If we specify a function in theparse_floatparameter, theload()method passes the string containing a floating point number to the function and the output of the function is used in the python object. This parameter can be used if you want to convert the floats to ints or other data types while loading the JSON itself. - The
parse_intparameter is used to convert any integer in the JSON to another data type. By default, theint()function is called with the strings containing integers in the JSON. If we specify a function in theparse_intparameter, theload()method passes the string containing the integer to the function and the output of the function is used in the python object. This parameter can be used if you want to convert the integers to floats or other data types while loading the JSON itself. The defaultparse_intofint()now limits the maximum length of the integer string via the interpreter’s integer string conversion length limitation to help avoid denial of service attacks. - The
parse_constantparameter is used to loadNaN,-Infinity, and+Infinityfrom JSON to custom python values. Theparse_constantparameter takes a function as its input argument. While the execution of theload()function,NaN,-Infinity, and+Infinityare passed to the function, and the return value is used in the python object. - The
object_pairs_hookis an optional parameter that takes a function as its input argument. The function is called with the result of any object literal decoded with an ordered list of pairs. The return value ofobject_pairs_hookis used instead of the dict. This feature can be used to implement custom decoders. Ifobject_hookis also defined, theobject_pairs_hooktakes priority.
After execution, the load() method returns a python object. For instance, consider the following JSON file.
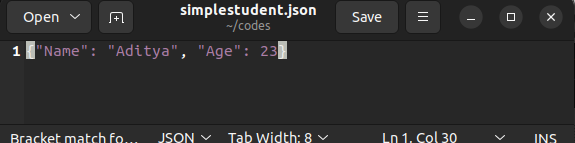
When we convert the above JSON file to a python object using the load() method, we will get a python dictionary.
You can convert JSON files to python objects using the load() method as shown below.
import json
fp=open("simplestudent.json","r")
myDict=json.load(fp)
print("The python object is:")
print(myDict)
fp.close()Output:
The python object is:
{'Name': 'Aditya', 'Age': 23}Convert JSON String to Python Object
To convert a JSON string to a python object, we can use the loads() method or the JSONDecoder class.
The loads() Method
The loads() method is used to load a JSON string into a python object. It has the following syntax.
json.loads(json_string, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)Here, the json_string parameter denotes the JSON string that has to be converted to a python object. All other parameters in the loads() method are the same as in the load() method. After execution, the loads() method returns a python object as shown below.
import json
jsonStr='{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}'
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)
myDict=json.loads(jsonStr)
print("The python object is:")
print(myDict)Output:
The JSON string is:
{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}
The python object is:
{'Name': 'Aditya', 'Age': 23}In this example, you can observe that we have converted a JSON string to a python dictionary using the loads() method.
JSON String to Python Dictionary Using JSONDecoder Class
The JSONDecoder class is used to create custom JSON decoders in Python. To convert a JSON string to a python object using the JSONDecoder class, we will first execute the JSONDecoder() constructor. The JSONDecoder constructor returns a JSONDecoder object after execution.
We will invoke the decode() method on the JSONDecoder object to create a python object from the JSON string. The decode() method takes a JSON string and returns a python object as shown in the following example.
import json
jsonStr='{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}'
print("The JSON string is:")
print(jsonStr)
myDict=json.JSONDecoder().decode(jsonStr)
print("The python object is:")
print(myDict)Output:
The JSON string is:
{"Name": "Aditya", "Age": 23}
The python object is:
{'Name': 'Aditya', 'Age': 23}By default, the load() method, loads() method and the decode() function return a python dictionary. To convert a JSON object directly into a custom python object, you can read this article on custom JSON decoder in Python.
Why Use JSON Files With Python for Data Transmission?
- The JSON Format is syntactically similar to primitive python objects. Hence, it is easy to convert a python object to JSON and send it over the network. To send custom python objects, we can define encoders and decoders and easily transmit data in JSON format.
- The JSON data is in text format. Hence, we can send it to any application. Also, it can be handled by any programming language as all programming languages support text data.
- The JSON format is extremely lightweight. It can easily be sent over HTTP and HTTPS due to its small size.
- JSON is easy to read, structured using key-value pairs, and doesn’t have many closing or opening tags unlike other formats such as XML.
- Almost every major language has dedicated libraries for handling JSON data. So, even if you are using different programming languages in different teams, your software modules can easily communicate with each other using JSON.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed working with JSON files in Python.To learn more about python programming, you can read this article on how to create a chat app in Python. You might also like this article on linear regression using the sklearn module in Python.
Stay tuned for more informative articles.
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

